Overloading
Overloading
Types
- Constructor Overloading: In Constructor Overloading multiple constructors has same name but different arguments.
- Method Overloading: Method Overloading is also called as Function Overloading. Overloading means a functions has different signatures defined and based on the arguments it can be difined which signature is to be used. Typical example of that is Consome.WriteLine in C# console which has many overloading defined. A Functions said to be overloaded When:
- Function has same Name but different return type
- Number of arguments are diffent
- Arguments have different return type
- Operator Overloading: Using operators we can perform operations on operands but sometimes operands have complex structure like what will happen if you want to add 2 objects based on a criteria or compare two objects based on a criteria and we will not be able to perform direct operations on them. So with the help of operator overloading we can change the operation of the existing operators.
Code
Overloading.cs
class Overloading
{
#region data
public enum PerformFunction
{
Int, String
}
public int Decider { get; private set; }
public int Num1 { get; private set; }
public int Num2 { get; private set; }
public string Str1 { get; private set; }
public string Str2 { get; private set; }
public PerformFunction Func { get; private set; }
#endregion data
#region Constructor Overloading
/// <summary>
/// Default Constructor
/// </summary>
public Overloading()
{
Console.WriteLine("\r\n*****Default Constructor******");
}
/// <summary>
/// Overloaded Constructor with 2 int value and 1 enum
/// </summary>
public Overloading(int num1, int num2, PerformFunction func)
{
Num1 = num1;
Num2 = num2;
Func = func;
Console.WriteLine("*****Overloaded '{2}' Constructor Called with {0} , {1} ******", num1,num2,func);
}
/// <summary>
/// Overloaded Constructor with 2 string value and 1 enum
/// </summary>
public Overloading(string str1,string str2, PerformFunction func)
{
Str1 = str1;
Str2 = str2;
Func = func;
Console.WriteLine("*****Overloaded '{2}' Constructor Called with {0} , {1} ******", str1, str2,func);
}
/// <summary>
/// Overloaded Constructor with 2 string value and 1 int value
/// </summary>
/// <param name="str1">Ignored not used for Operaotor Overloading Demonstration</param>
/// <param name="str2">Ignored not used for Operaotor Overloading Demonstration</param>
/// <param name="decider"> Value of this will decide which object is greater</param>
public Overloading(string str1, string str2, int decider)
{
Str1 = str1;
Str2 = str2;
Decider = decider;
Console.WriteLine("\r\n*****Overloaded Operator Constructor Called with {0} , {1} , {2} ******", str1, str2, decider);
}
#endregion
#region Function Overloading
/// <summary>
/// Overloaded method with 2 int value and this method should ADD both values and print the result
/// </summary>
/// <param name="num1"></param>
/// <param name="num2"></param>
public int Add(int num1,int num2)
{
return num1 + num2;
}
/// <summary>
/// Overloaded method with 2 string value and this method should CONCATENATE both values and print the result
/// </summary>
/// <param name="str1"></param>
/// <param name="str2"></param>
public string Add(string str1, string str2)
{
return str1 + str2;
}
/// <summary>
/// Overloaded method will check the data in the object and will use the values present in the object to perform the function based on the 'PerformFunction' enum i.e. either ADD or CONCATENATE
/// </summary>
/// <param name="ns1"></param>
public string Add(Overloading ns1)
{
if(ns1.Func == PerformFunction.Int)
return (ns1.Num1 + ns1.Num2).ToString();
else if (ns1.Func == PerformFunction.String)
return ns1.Str1 + ns1.Str2;
return string.Empty;
}
#endregion Function Overloading
#region Operator Overloading
/// <summary>
/// This method will look at the decider value of passed objects to compare which object is bigger
/// </summary>
/// <param name="ns1"></param>
/// <param name="ns2"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static bool operator >(Overloading ns1, Overloading ns2)
{
var result = ns1.Decider > ns2.Decider;
return result;
}
/// <summary>
/// This method will look at the decider value of passed objects to compare which object is smaller
/// </summary>
/// <param name="ns1"></param>
/// <param name="ns2"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static bool operator <(Overloading ns1, Overloading ns2)
{
var result = ns1.Decider < ns2.Decider;
return result;
}
#endregion Operator Overloading
}
{
#region data
public enum PerformFunction
{
Int, String
}
public int Decider { get; private set; }
public int Num1 { get; private set; }
public int Num2 { get; private set; }
public string Str1 { get; private set; }
public string Str2 { get; private set; }
public PerformFunction Func { get; private set; }
#endregion data
#region Constructor Overloading
/// <summary>
/// Default Constructor
/// </summary>
public Overloading()
{
Console.WriteLine("\r\n*****Default Constructor******");
}
/// <summary>
/// Overloaded Constructor with 2 int value and 1 enum
/// </summary>
public Overloading(int num1, int num2, PerformFunction func)
{
Num1 = num1;
Num2 = num2;
Func = func;
Console.WriteLine("*****Overloaded '{2}' Constructor Called with {0} , {1} ******", num1,num2,func);
}
/// <summary>
/// Overloaded Constructor with 2 string value and 1 enum
/// </summary>
public Overloading(string str1,string str2, PerformFunction func)
{
Str1 = str1;
Str2 = str2;
Func = func;
Console.WriteLine("*****Overloaded '{2}' Constructor Called with {0} , {1} ******", str1, str2,func);
}
/// <summary>
/// Overloaded Constructor with 2 string value and 1 int value
/// </summary>
/// <param name="str1">Ignored not used for Operaotor Overloading Demonstration</param>
/// <param name="str2">Ignored not used for Operaotor Overloading Demonstration</param>
/// <param name="decider"> Value of this will decide which object is greater</param>
public Overloading(string str1, string str2, int decider)
{
Str1 = str1;
Str2 = str2;
Decider = decider;
Console.WriteLine("\r\n*****Overloaded Operator Constructor Called with {0} , {1} , {2} ******", str1, str2, decider);
}
#endregion
#region Function Overloading
/// <summary>
/// Overloaded method with 2 int value and this method should ADD both values and print the result
/// </summary>
/// <param name="num1"></param>
/// <param name="num2"></param>
public int Add(int num1,int num2)
{
return num1 + num2;
}
/// <summary>
/// Overloaded method with 2 string value and this method should CONCATENATE both values and print the result
/// </summary>
/// <param name="str1"></param>
/// <param name="str2"></param>
public string Add(string str1, string str2)
{
return str1 + str2;
}
/// <summary>
/// Overloaded method will check the data in the object and will use the values present in the object to perform the function based on the 'PerformFunction' enum i.e. either ADD or CONCATENATE
/// </summary>
/// <param name="ns1"></param>
public string Add(Overloading ns1)
{
if(ns1.Func == PerformFunction.Int)
return (ns1.Num1 + ns1.Num2).ToString();
else if (ns1.Func == PerformFunction.String)
return ns1.Str1 + ns1.Str2;
return string.Empty;
}
#endregion Function Overloading
#region Operator Overloading
/// <summary>
/// This method will look at the decider value of passed objects to compare which object is bigger
/// </summary>
/// <param name="ns1"></param>
/// <param name="ns2"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static bool operator >(Overloading ns1, Overloading ns2)
{
var result = ns1.Decider > ns2.Decider;
return result;
}
/// <summary>
/// This method will look at the decider value of passed objects to compare which object is smaller
/// </summary>
/// <param name="ns1"></param>
/// <param name="ns2"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static bool operator <(Overloading ns1, Overloading ns2)
{
var result = ns1.Decider < ns2.Decider;
return result;
}
#endregion Operator Overloading
}
Program.cs
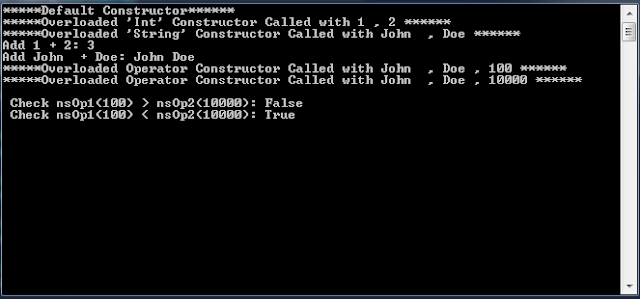
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Default Constructor Called
Overloading ns1 = new Overloading();
//Overloaded Constructor Called with Int
Overloading nsInt = new Overloading(1,2,PerformFunction.Int);
//String Constructor Called with String
Overloading nsString = new Overloading( "John ", "Doe", PerformFunction.String);
//Calling Overloaded Method for Interger
Console.WriteLine("\r\n Overload Func 1.1('{2}') - Add {0} > {1} : {3}", nsInt.Num1, nsInt.Num2, nsInt.Func, ns1.Add(nsInt));
//Calling Overloaded Method for Interger
Console.WriteLine("\r\n Overload Func 1.2('{2}') - Add {0} > {1} : {3}", nsString.Str1, nsString.Str2, nsString.Func, ns1.Add(nsString));
//Called overloaded method without object and with 2 intergers
Console.WriteLine("\r\n Overload Func 2 - Add {0} > {1} : {2}", 1234, 8978, ns1.Add(1234, 8978));
//Called overloaded method without object and with 2 strings
Console.WriteLine("\r\n Overload Func 3 - Add {0} > {1} : {2}", "Hello ", "World", ns1.Add("Hello ", "World"));
//String Constructor Called with String
Overloading nsOp1 = new Overloading("John ", "Doe", 100);
Overloading nsOp2 = new Overloading("John ", "Doe", 10000);
//Calling Overloaded operator
var result = nsOp1 > nsOp2;
Console.WriteLine("\r\n Check nsOp1({0}) > nsOp2({1}): {2}", nsOp1.Decider, nsOp2.Decider, result);
result = nsOp1 < nsOp2;
Console.WriteLine("\r\n Check nsOp1({0}) < nsOp2({1}): {2}", nsOp1.Decider, nsOp2.Decider, result);
Console.ReadLine();
}
{
//Default Constructor Called
Overloading ns1 = new Overloading();
//Overloaded Constructor Called with Int
Overloading nsInt = new Overloading(1,2,PerformFunction.Int);
//String Constructor Called with String
Overloading nsString = new Overloading( "John ", "Doe", PerformFunction.String);
//Calling Overloaded Method for Interger
Console.WriteLine("\r\n Overload Func 1.1('{2}') - Add {0} > {1} : {3}", nsInt.Num1, nsInt.Num2, nsInt.Func, ns1.Add(nsInt));
//Calling Overloaded Method for Interger
Console.WriteLine("\r\n Overload Func 1.2('{2}') - Add {0} > {1} : {3}", nsString.Str1, nsString.Str2, nsString.Func, ns1.Add(nsString));
//Called overloaded method without object and with 2 intergers
Console.WriteLine("\r\n Overload Func 2 - Add {0} > {1} : {2}", 1234, 8978, ns1.Add(1234, 8978));
//Called overloaded method without object and with 2 strings
Console.WriteLine("\r\n Overload Func 3 - Add {0} > {1} : {2}", "Hello ", "World", ns1.Add("Hello ", "World"));
//String Constructor Called with String
Overloading nsOp1 = new Overloading("John ", "Doe", 100);
Overloading nsOp2 = new Overloading("John ", "Doe", 10000);
//Calling Overloaded operator
var result = nsOp1 > nsOp2;
Console.WriteLine("\r\n Check nsOp1({0}) > nsOp2({1}): {2}", nsOp1.Decider, nsOp2.Decider, result);
result = nsOp1 < nsOp2;
Console.WriteLine("\r\n Check nsOp1({0}) < nsOp2({1}): {2}", nsOp1.Decider, nsOp2.Decider, result);
Console.ReadLine();
}
Output
Explanation
Please look into the comments and summaries to understand overloading

Comments
Post a Comment